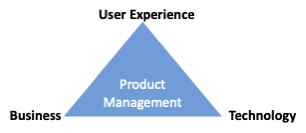
Product Management
Product Management is an function that guides every step of a product’s lifecycle, from proposal, to positioning and pricing - focusing on customers, what attracts them to the product, and how value will be generated.

Companies need an intimate understanding of customers and the ability to create tailored solutions for them - Product Management is a vital role that guides every step of a product’s lifecycle, from proposal, to positioning and pricing - focusing on customers and how value will be generated.
Product Managers advocate for customers within the organisation and make sure the voice of the market is heard and heeded.

Product Managers also work closely with teams interacting with customers, as well as creating Products within an overall enterprise architecture which are built by ring-fenced engineering teams reporting into them.
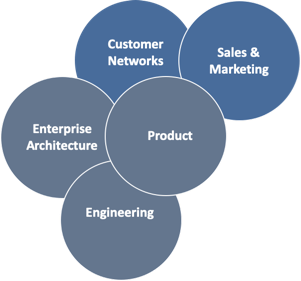
Thanks to this focus on the customer, product aware organisations deliver better-designed, higher-performing products.
Product Managers need 3 further skills:
- Storytelling – so that they can share their knowledge of the customer
- Marketing – to integrate the language of customers into product messaging
- Empathy – for engineers and how they work; for customers and their pain points, and even for upper management, who juggle aggressive goals and impossible schedules.
Product managers are responsible for product vision, market research, competitive analysis, target market understanding and customer requirements, plus a roadmap of how to deliver the value.
Next:
We discuss how each major cross-functional capability works in a customer-centric world in these other posts:


A customer's response to your product is their sub-conscious alignment their unrealised needs, expectations, requirements and motivations. We explore this further in What are your Product Benefits?

Building a customer-centric digital organisation that is focused on delivering value to your customers needs new and agile ways of working. We explore this thinking in The Three Laws.


